How To Create A Data Structure Representing A Polymorphic Tree
If I had to selection the unmarried most of import topic in software development, it would be data structures. Ane of the most common and easiest ones is a tree – a hierarchical data structure. In this commodity, let's explore Trees in Java.
- What is a Binary Tree?
- Types of Binary Tree
- Binary Tree Implementation
- Tree Traversals
- Applications of Binary Tree
What is a Binary Tree?
A Tree is a non-linear data construction where data objects are generally organized in terms of hierarchical relationship. The structure is non-linear in the sense that, unlike Arrays, Linked Lists, Stack and Queues, information in a tree is not organized linearly. A binary tree is a recursive tree data structure where each node can have 2 children at most.
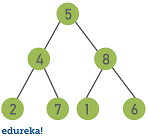
Binary copse have a few interesting properties when they're perfect:
- Holding 1: The number of total nodes on each "level" doubles as you lot motion downwards the tree.
- Belongings 2: T he number of nodes on the last level is equal to the sum of the number of nodes on all other levels, plus one
Each information element stored in a tree construction called a node. A Tree node contains the following parts:
1. Data
2. Pointer to left kid
3. Pointer to the right child
In Java, we tin correspond a tree node using class. Below is an example of a tree node with integer data.
static class Node { int value; Node left, correct; Node(int value){ this.value = value; left = null; right = aught; } Now that you know what is a binary tree, let'due south bank check out unlike types of binary trees.
Types of Binary Trees
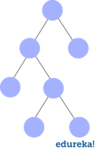
Total Binary Tree
Atotal binary treeis a binary tree where every node has exactly 0 or 2 children. The case of fully binary tress is:
Perfect Binary Tree
A binary tree is perfect binary Tree if all internal nodes have ii children and all leaves are at the same level. The example of perfect binary tress is:

Consummate Binary Tree
Aconsummate binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are equally far left as possible. An example of a complete binary tree is:

At present that yous are aware of dissimilar types of binary trees, let'due south cheque out how to create a binary tree.
Binary Tree Implementation
For the implementation, there's an auxiliary Node form that will shop int values and keeps a reference to each kid. The first step is to find the place where nosotros want to add a new node in society to keep the tree sorted. Nosotros'll follow these rules starting from the root node:
- if the new node'south value is lower than the current node'southward, go to the left child
- if the new node'due south value is greater than the current node'south, become to the right child
- when the electric current node is null, we've reached a leaf node, nosotros insert the new node in that position
At present let'due south see how we tin can implement this logic with the help of an example:
package MyPackage; public class Tree { static class Node { int value; Node left, right; Node(int value){ this.value = value; left = null; right = cipher; } } public void insert(Node node, int value) { if (value < node.value) { if (node.left != zilch) { insert(node.left, value); } else { Organisation.out.println(" Inserted " + value + " to left of " + node.value); node.left = new Node(value); } } else if (value > node.value) { if (node.right != aught) { insert(node.right, value); } else { Organization.out.println(" Inserted " + value + " to right of " + node.value); node.right = new Node(value); } } } public void traverseInOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { traverseInOrder(node.left); System.out.print(" " + node.value); traverseInOrder(node.right); } } public static void principal(String args[]) { Tree tree = new Tree(); Node root = new Node(5); System.out.println("Binary Tree Example"); Organization.out.println("Building tree with root value " + root.value); tree.insert(root, ii); tree.insert(root, 4); tree.insert(root, 8); tree.insert(root, vi); tree.insert(root, 7); tree.insert(root, three); tree.insert(root, nine); Organization.out.println("Traversing tree in order"); tree.traverseLevelOrder(); } } Output:
Binary Tree Instance Building tree with root value 5 Inserted 2 to left of 5 Inserted 4 to right of ii Inserted viii to right of v Inserted six to left of eight Inserted 7 to correct of vi Inserted 3 to left of iv Inserted 9 to right of eight Traversing tree in guild 2 iii 4 five 6 7 8 9
In this case, we have used in-lodge traversal to traverse the tree. The in-guild traversal consists of first visiting the left sub-tree, and then the root node, and finally the right sub-tree. There are more than ways to traverse a tree. Allow'due south check them out.
Tree Traversals
Trees can exist traversed in several means: Let's utilise the aforementioned tree case that we used before for each example.
Depth Commencement Search
Depth-first search is a type of traversal where you become as deep equally possible downwards one path before bankroll up and trying a unlike one. There are several ways to perform a depth-first search: in-order, pre-order and mail service-order.
We already checked out in-order traversal. Let'south check out pre-order and mail-order now.
Pre-Order Traversal
In Pre-order traversal yous visit the root node first, so the left subtree, and finally the right subtree. Here's the lawmaking.
public void traversePreOrder(Node node) { if (node != null) { Organization.out.print(" " + node.value); traversePreOrder(node.left); traversePreOrder(node.right); } } Output:
5 ii 4 3 eight 6 7 ix
Post-Club Traversal
In Post-order traversal you visit left subtree first, then the right subtree, and the root node at the end. Here'south the code.
public void traversePostOrder(Node node) { if (node != cypher) { traversePostOrder(node.left); traversePostOrder(node.right); System.out.impress(" " + node.value); } } Output:
3 four 2 seven 6 ix 8 5
Breadth-Start Search
This type of traversal visits all the nodes of a level earlier going to the next level. It is similar throwing a stone in the eye of a pond. The nodes you explore "ripple out" from the starting bespeak. Breadth-First Search is also called level-club and visits all the levels of the tree starting from the root, and from left to right.
Applications of Binary Tree
Applications of binary trees include:
- Used in many search applications where data is constantly inbound/leaving
- As a workflow for compositing digital images for visual effects
- Used in almost every high-bandwidth router for storing router-tables
- Also used in wireless networking and memory allocation
- Used in pinch algorithms and many more
This brings united states to the terminate of this 'Trees in Java' commodity.
Make certain you exercise as much every bit possible and revert your experience.
Cheque out the Java Online Course by Edureka, a trusted online learning company with a network of more than 250,000 satisfied learners spread across the earth. We are here to assist you lot with every step on your journey, for becoming a besides this java interview questions, we come up with a curriculum which is designed for students and professionals who want to be a Coffee Developer.
Got a question for united states of america? Please mention it in the comments section of this 'Trees in Java' article and we volition go back to yous every bit soon as possible or yous tin can also join our Coffee Training in Ernakulam.
How To Create A Data Structure Representing A Polymorphic Tree,
Source: https://www.edureka.co/blog/java-binary-tree
Posted by: woodmomenten1943.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Create A Data Structure Representing A Polymorphic Tree"
Post a Comment